Java - Programming Fundamentals (Part 4)
We have created our initial classes, so now we want to compile the classes. In order to do that we open the command line (To open command line, go to start menu, click on run, type “cmd” and press ok).Use the command “javac” to compile.
$ javac
bash: javac: command not found
Oops! We got a serious problem here, the command line does not recognize the javac command. To resolve this issue we need to add the environment variables.
Setting up Environment varaibles
Set the path using the command:-
// on windows:
set path=c:\program files\Java\jdk1.6_0_16\bin
// on linux
export PATH=$PATH:<JDK Location>/bin
(provide the location of
now when you type javac, you will get output something like this
$ javac
Usage: javac <options> <source files>
where possible options include:
-g Generate all debugging info
-g:none Generate no debugging info
-g:{lines,vars,source} Generate only some debugging info
-nowarn Generate no warnings
-verbose Output messages about what the compiler is doing
-deprecation Output source locations where deprecated APIs are used
-classpath <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotation processors
-cp <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotation processors
-sourcepath <path> Specify where to find input source files
-bootclasspath <path> Override location of bootstrap class files
-extdirs <dirs> Override location of installed extensions
-endorseddirs <dirs> Override location of endorsed standards path
-proc:{none,only} Control whether annotation processing and/or compilation is done.
-processor <class1>[,<class2>,<class3>...] Names of the annotation processors to run;
bypasses default discovery process
-processorpath <path> Specify where to find annotation processors
-parameters Generate metadata for reflection on method parameters
-d <directory> Specify where to place generated class files
-s <directory> Specify where to place generated source files
-h <directory> Specify where to place generated native header files
-implicit:{none,class} Specify whether or not to generate class files for
implicitly referenced files
-encoding <encoding> Specify character encoding used by source files
-source <release> Provide source compatibility with specified release
-target <release> Generate class files for specific VM version
-profile <profile> Check that API used is available in the specified profile
-version Version information
-help Print a synopsis of standard options
-Akey[=value] Options to pass to annotation processors
-X Print a synopsis of nonstandard options
-J<flag> Pass <flag> directly to the runtime system
-Werror Terminate compilation if warnings occur
@<filename> Read options and filenames from file
The environment variables can also be added by adding to the system environment variables on windows:-
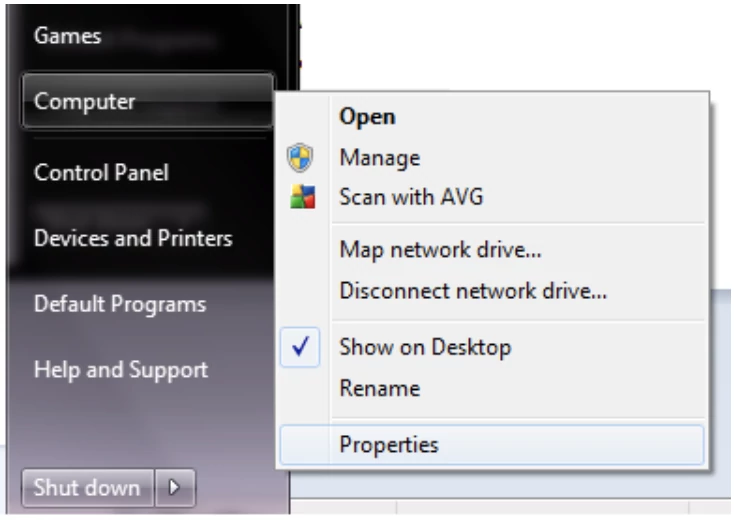
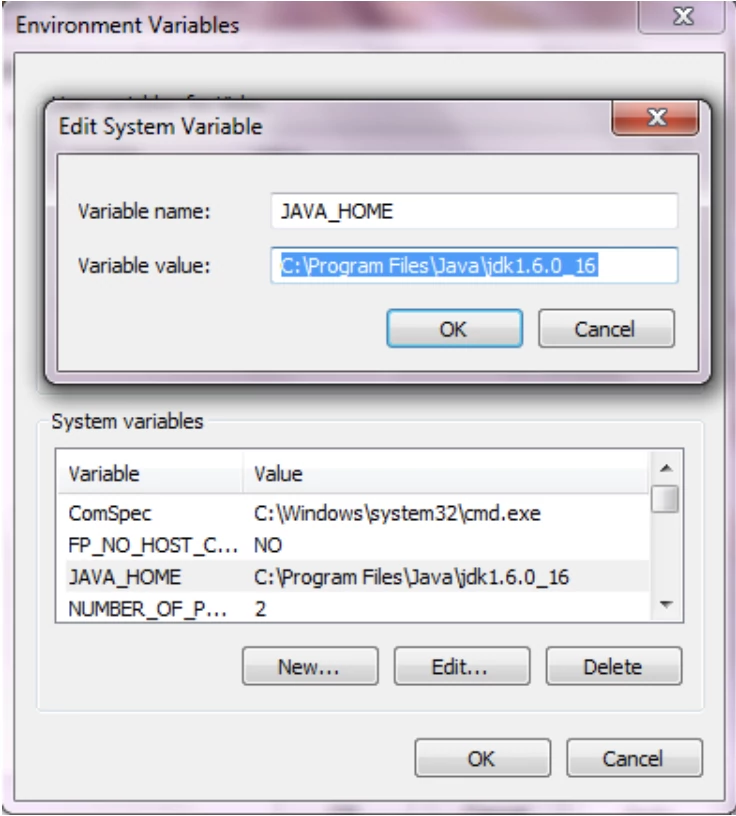
Go to Computer -> properties -> Environment Variables add a new variable JAVA_HOME and add the path to
Compiling the program
Now the Environment variables have been added and we have to compile the program.
$ javac RunnerClass.java
When you compile the main class i.e. RunnerClass.java the subordinate class gets compile automatically (Person class). You will observe that two .class files are created.
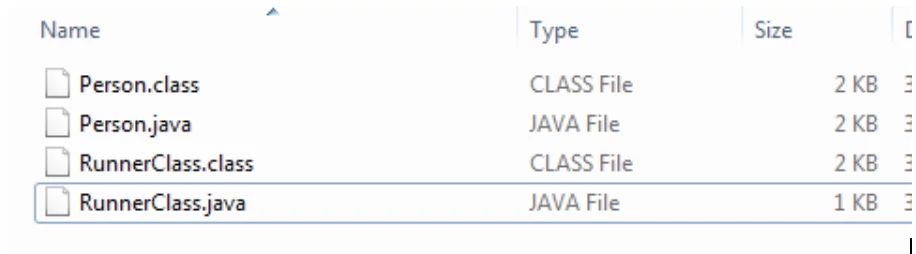
The every java file is converted into a bytecode and is represented as .class files.
Execute
Once the program is compiled, we are ready to execute the program. To run the program type java followed by the class name (which has the main method). Do not append .class at the end of the command.
$ java RunnerClass
Default constructor
Account Number = null
Balance = 5000.0
***********************************
Passing the one parameter
Account Number = 12345
Balance = 5000.0
***********************************
Passing two parameters
Account Number = 123
Balance = 50.0
***********************************
If you liked this article, you can buy me a coffee
Leave a comment