Java - Loop
You may encounter situations, when a block of code needs to be executed several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on.
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times.
While Statement
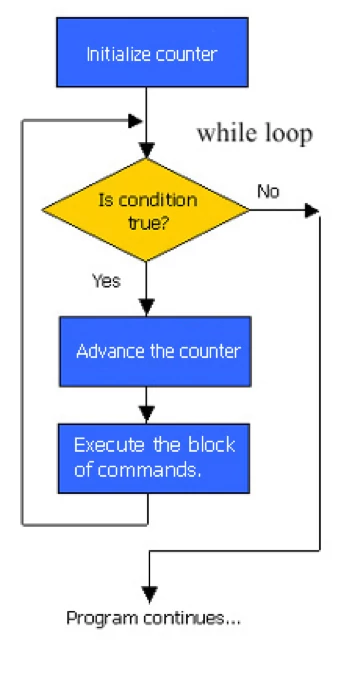
The while statement is a loop construct control statement that executes a block of code while a condition is true. You can either have a single statement or a block of code within the while loop. The loop will never be executed if the testing expression evaluates to false. The loop condition must evaluate to a Boolean result.
The syntax of the while loop is
while (<loop condition>){
<statements>
}
public class WhileLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 1;
System.out.println("Printing Numbers from 1 to 10");
while (count <= 10) {
count = count + 1;
System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
Printing Numbers from 1 to 10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Do-while Loop Statement
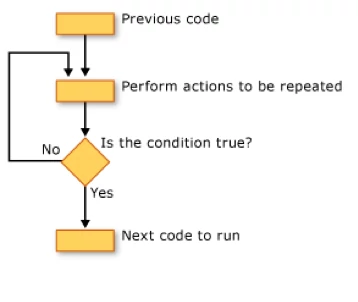
The do-while loop is similar to the while loop, except that the test is performed at the end of the loop instead of at the beginning. This ensures that the loop will be executed at least once. A do-while loop begins with the keyword do, followed by the statements that make up the body of the loop. Finally, the keyword while and the test expression completes the do-while loop. When the loop condition becomes false, the loop is terminated and execution continues with the statement immediately following the loop. You can either have a single statement or a block of code within the do-while loop.
The syntax of the do-while loop is:
do
<loop body>
while (<loop condition>);
public class DoWhileLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 1;
System.out.println("Printing Numbers from 1 to 10");
do {
System.out.println(count++);
} while (count <= 10);
}
}
Printing Numbers from 1 to 10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
For Loops
The for loop is a looping construct which can execute a set of instructions a specified number of times. It’s a counter controlled loop.
The syntax of the loop is as follows:
for (<initialization>; <loop condition>; <increment expression>)
<loop body>
The first part of a for statement is a starting initialization, which executes once before the loop begins. The
All the sections in the for-header are optional. Any one of them can be left empty, but the two semicolons are mandatory. In particular, leaving out the

public class ForLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1
22
333
4444
55555
If you liked this article, you can buy me a coffee
Leave a comment