Github gives a generous limits for your private projects, its to good for your private repos or even small startups. However, Github package has a constraint of 500mb size, which is quite low.
Lets compare the pricing for both github & gcp (as of July 2021)
| Storage (per GB) | Data Transfer (per GB) | |
|---|---|---|
| Github | $0.25 | $0.50 |
| GCP artifactory | $0.10 | $0.01 - $0.15 |
Looking at pricing, storing artifacts in GCP is a good idea.
Setting up service account
The first thing, we need to set up our service account, so that github has required permission to publish the packages.
Login to google console and navigate to `IAM
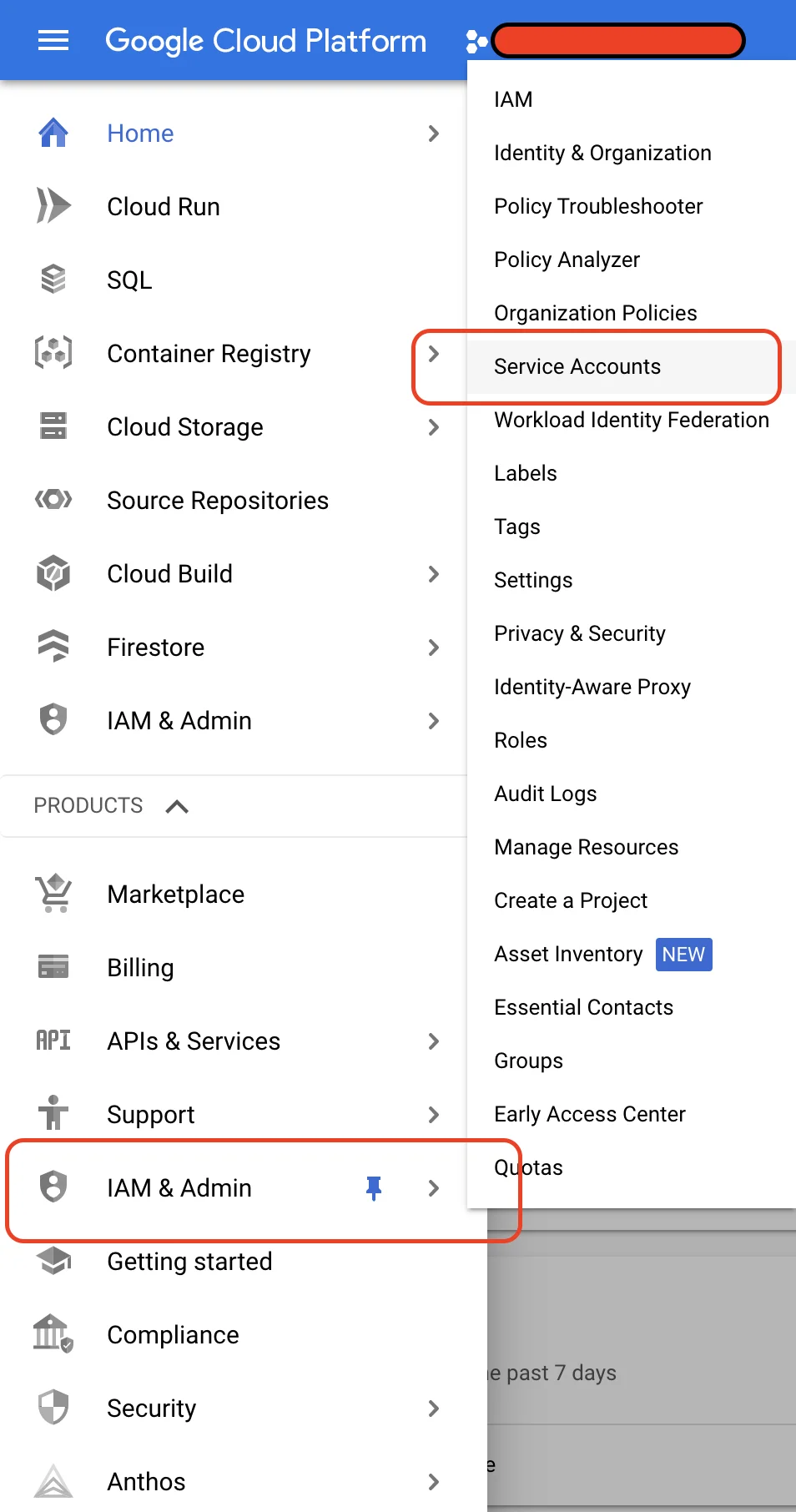
You need to add following permission for publishing artifacts (optionally you can provide Cloud Run Service Agent for
cloud run deployments)

Then generate & download key in json format
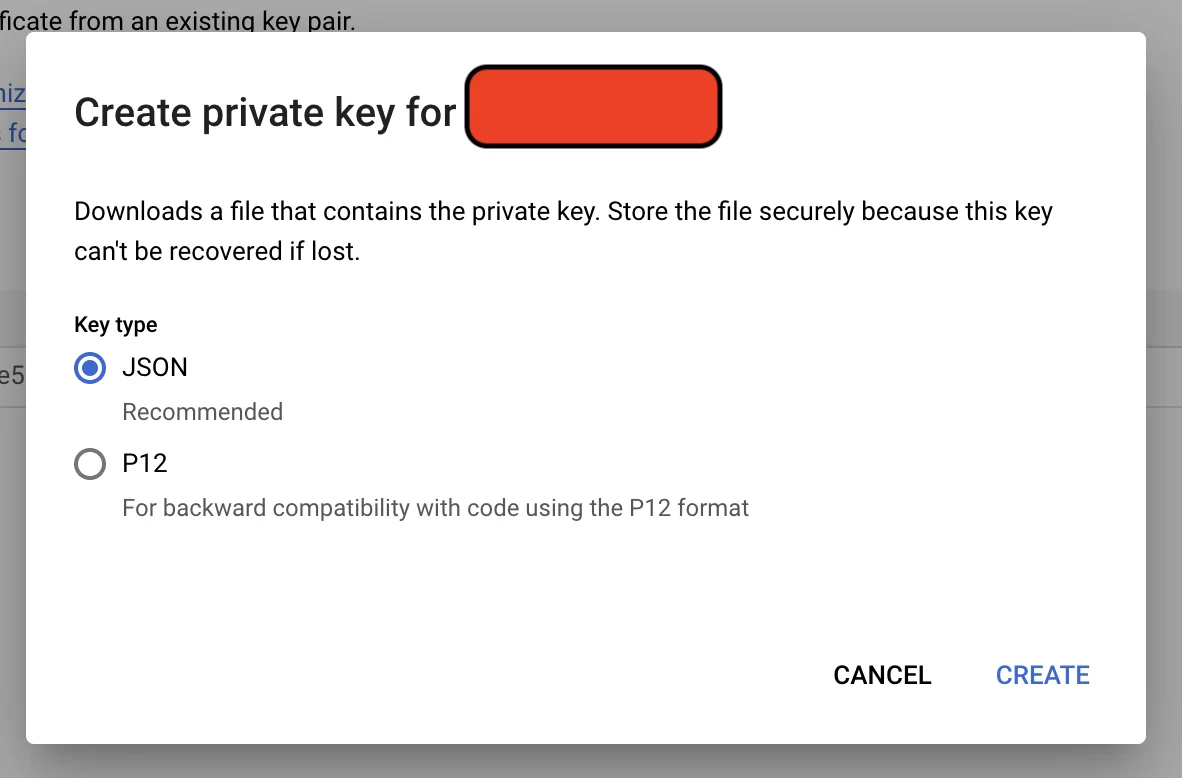
Setup Tokens
The first step is to set up a personal access token.
Go to your profile and click to settings.
Go to developer section
Add a new token GCP_ARTIFACTORY_SERVICE_ACCOUNT with the contents for download service account key. Also add another
token GCP_PROJECT_ID with your GCP project id.
Github Action
Time to setup a github action to push artifacts to repository. You will need to add .github/workflows/ci.yaml
There are 5 steps here:
- Checkout the project
- Next we are setting up GCP credentials
- Although not required, but in step 3, we are caching the .m2 folder to speed up the builds
- We are setting up Java 11
- Finally, we are deploying our package to the artifactory.
We are using -DaltReleaseDeploymentRepository argument of maven to point to our artifactory.
Using dependencies from gcp artifactory
In order to use the artifacts, you need to specify the repository in your pom file
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>artifact-registry</id>
<url>artifactregistry://<YOUR-ARTIFACTORY-REPO></url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
We will also need to add wagon extension for GCP in your pom file:
<build>
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.artifactregistry</groupId>
<artifactId>artifactregistry-maven-wagon</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
</build>
Using parent from your artifactory
Finally, if want to extend from parent POM from your artifactory. You will have create .mvn/extensions.xml.
This is required because the extensions are not build to load parent pom, so it has to be run in the pre-build step.
And, there you have it, publish & use artifacts from GCP
If you liked this article, you can buy me a coffee
Leave a comment